Jul 01,2022
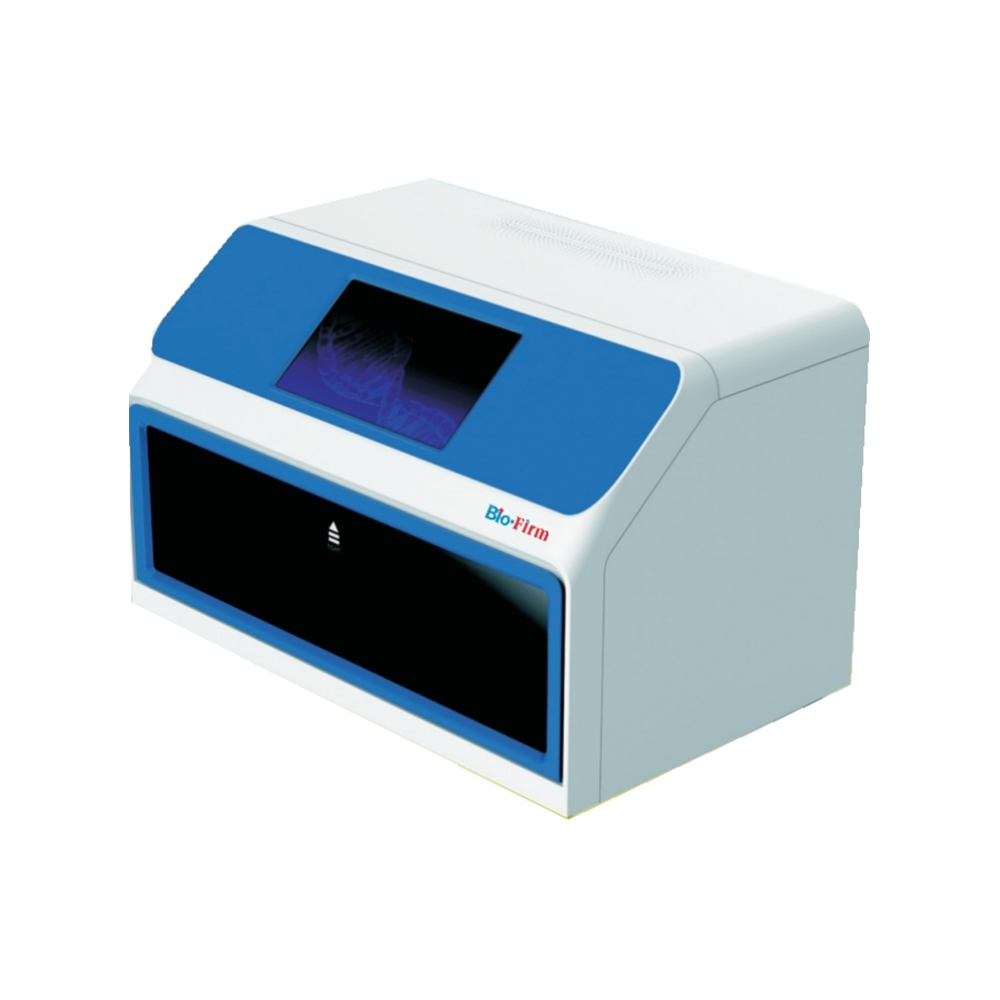
Yes, the WNE-96 Nucleic Acid Purification Instrument typically includes several features designed to minimize cross-contamination between samples. These features are critical for ensuring the integrity and reliability of nucleic acid purification, especially in high-throughput environments where many samples are processed simultaneously. Here are some common features that help reduce cross-contamination:
Disposable Tips:
The nucleic acid purification instrument WNE-96 often uses single-use, disposable tips for liquid handling. This ensures that each sample is processed with a fresh tip, reducing the risk of carryover contamination between samples.
Some systems also use filter tips , which have an additional barrier to prevent aerosols or liquids from entering the pipetting mechanism.
UV Sterilization:
Many automated nucleic acid purification instruments, including the WNE-96, come equipped with UV sterilization capabilities. After each run, the instrument can perform a UV light cycle to disinfect the internal workspace, killing any residual nucleic acids or contaminants that may be present.
This feature is particularly useful for preventing contamination in subsequent runs.
Enclosed System:
The WNE-96 operates as a closed system , meaning that samples are contained within the instrument during processing. This minimizes the exposure of samples to the external environment, reducing the risk of airborne contaminants or human error.
Enclosed systems also help maintain sterility and prevent contamination from external sources, such as dust or aerosols.
Automated Wash Steps:
The instrument typically includes automated wash steps during the purification process. These washes are designed to remove impurities, including potential contaminants, from the magnetic beads or columns used for nucleic acid binding.
Multiple wash cycles ensure that any residual contaminants are thoroughly removed before elution of the purified nucleic acids.

Separate Reagent Channels:
The WNE-96 often has dedicated reagent channels for different solutions (e.g., lysis buffer, wash buffer, elution buffer). This prevents mixing of reagents and reduces the risk of cross-contamination between different steps of the purification process.
Some systems also allow for reagent tracking , ensuring that the correct reagents are used at the right time and in the correct amounts.
HEPA Filtration (Optional):
Some models of the WNE-96 may include HEPA filtration systems to further reduce the risk of airborne contaminants entering the instrument during operation. HEPA filters are highly effective at capturing small particles, including microorganisms and nucleic acid fragments.
Software-Controlled Protocols:
The instrument's software can be programmed to follow strict protocols that minimize the risk of cross-contamination. For example, the software can ensure that tips are changed at appropriate intervals, that wash steps are performed thoroughly, and that the UV sterilization cycle is activated after each run.
Additionally, the software can log each step of the process, providing traceability and ensuring that contamination prevention measures are consistently applied.
Magnetic Bead Technology:
If the nucleic acid purification instrument WNE-96 uses magnetic bead-based purification , this method inherently reduces the risk of cross-contamination compared to traditional column-based methods. Magnetic beads are confined to specific wells or tubes during processing, minimizing the chance of sample-to-sample contamination.
The beads can be washed multiple times within the same well, further reducing the risk of contamination.
Sample Tracking and Barcoding:
The WNE-96 may support sample tracking through barcodes or RFID tags, ensuring that each sample is processed independently and correctly. This helps prevent mix-ups or accidental cross-contamination between samples.
Sample tracking also provides a clear audit trail, which is essential for maintaining data integrity in regulated environments.
10. Regular Maintenance Alerts:
The instrument may have built-in alerts to remind users when maintenance tasks, such as cleaning or replacing parts, are due. Regular maintenance helps ensure that the instrument remains free of contaminants and operates efficiently.


 Español
Español
 Français
Français
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 عربى
عربى