Jul 01,2022
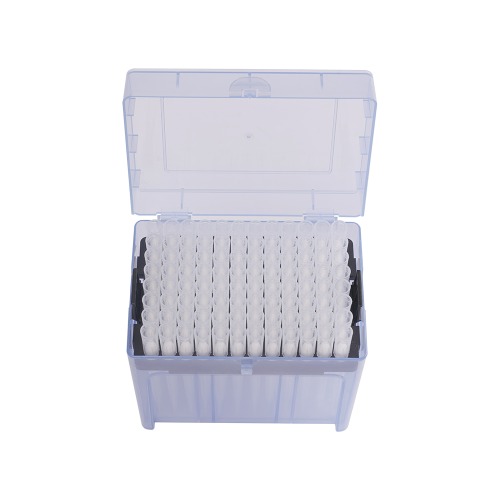
Manual pipette tips are disposable attachments used in conjunction with manual pipettes for accurate and precise liquid handling in laboratories and various scientific applications. They come in different sizes, shapes, and materials to accommodate various pipetting needs. Here are some common classifications of manual pipette tips:
Volume capacity: Manual pipette tips are often classified based on their volume capacity. They are available in a wide range of sizes, from microliters (µL) to milliliters (mL). Common volume capacities include 10 µL, 200 µL, 1000 µL, and 5 mL, among others. The volume capacity of the pipette tip should match the pipette's volume range to ensure accurate pipetting.
Tip shape: Manual pipette tips can have different shapes at the end that comes into contact with the liquid. The most common tip shapes include standard or conical tips and specialty tips like beveled tips or wide-bore tips. The choice of tip shape depends on the specific application requirements, such as precision, sample type, and compatibility with different containers.
Filtered or non-filtered: Pipette tips can be classified as filtered or non-filtered. Filtered tips have built-in filters that prevent the entry of contaminants, aerosols, or liquids into the pipette shaft. They are commonly used when working with sensitive samples or when pipetting liquids that can potentially contaminate the pipette. Non-filtered tips do not have built-in filters and are suitable for general-purpose applications.
Material: Manual pipette tips are typically made from polypropylene (PP), which is a widely used material due to its chemical compatibility, low retention, and inertness. However, there are also pipette tips made from other materials, such as low-retention or ultra-low-retention tips made from specialty polymers. These materials reduce sample retention on the tip's inner surface, ensuring maximum sample recovery.
Sterile or non-sterile: Manual pipette tips can be classified as sterile or non-sterile. Sterile tips undergo a sterilization process, such as gamma irradiation, to eliminate any potential microbial contamination. They are commonly used in applications where maintaining sample integrity and preventing cross-contamination are critical, such as in molecular biology, cell culture, and diagnostic assays. Non-sterile tips are suitable for general laboratory use where sterility is not a requirement.
Compatibility: Manual pipette tips are designed to be compatible with specific brands or models of pipettes. Different pipette manufacturers may have their own proprietary tip designs or locking mechanisms. It is important to select pipette tips that are compatible with the specific pipette model to ensure proper attachment and reliable performance.
Besides,here are some common uses of manual pipette tips:
Liquid dispensing: Manual pipette tips are primarily used for accurately dispensing liquids from one container to another. They are commonly used in applications such as sample preparation, dilution, mixing, and aliquoting of reagents, buffers, chemicals, or biological samples.
Pipetting into microplates: Manual pipette tips are frequently used for pipetting into microplates, also known as microtiter plates or well plates. Microplates consist of multiple wells arranged in a grid format, and the precise and controlled delivery of liquid into these wells is crucial for various applications, including high-throughput screening, enzyme assays, and cell-based experiments.
Sample transfers: Manual pipette tips are employed for transferring samples from one vessel to another. This includes transferring samples from tubes, vials, or containers to other tubes or reaction vessels for further analysis or processing. They are commonly used in molecular biology, biochemistry, microbiology, and other research areas.
Accuracy and precision: Manual pipette tips play a vital role in achieving accurate and precise liquid handling. They allow scientists and technicians to control the volume of liquid being transferred with high precision, ensuring that the intended volume is dispensed accurately. This is critical for achieving consistent and reliable results in experiments, assays, and other laboratory procedures.
Minimizing cross-contamination: The disposable nature of manual pipette tips helps minimize the risk of cross-contamination between samples and reagents. After each use, the pipette tips can be discarded, eliminating the need for time-consuming and potentially error-prone cleaning and decontamination procedures. This is especially important when working with sensitive samples, DNA, RNA, or substances that could carry contaminants.
Compatibility with different liquids: Manual pipette tips are compatible with a wide range of liquids, including aqueous solutions, organic solvents, acids, bases, and biological samples. The materials used in the construction of pipette tips, such as polypropylene, ensure chemical resistance and compatibility with diverse liquid types, allowing for versatile use in various laboratory applications.
Sterile applications: Sterile manual pipette tips are used in applications that require aseptic conditions to prevent contamination. They are commonly used in cell culture, microbiology, and molecular biology experiments to ensure the integrity and purity of samples and reagents. Sterile pipette tips help maintain cell viability, minimize the risk of microbial contamination, and support sensitive assays and analyses.




 Español
Español
 Français
Français
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 عربى
عربى