Jul 01,2022
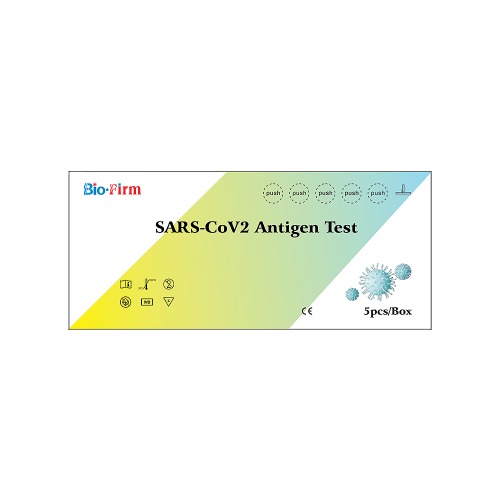
The SARS-CoV-2 antigen test kit is a diagnostic tool used to detect the presence of antigens specific to the SARS-CoV-2 virus, which causes COVID-19. Antigen tests are designed to identify active infections by detecting viral proteins in respiratory samples.
The working principle of a SARS-CoV-2 antigen test kit typically involves the following steps:
Sample Collection: A respiratory sample, usually obtained through a nasopharyngeal or nasal swab, is collected from the individual suspected of having a COVID-19 infection.
Extraction: The test kit includes reagents and materials to extract viral antigens from the collected sample. This step helps release the target antigens from the viral particles present in the sample.
Reaction: The extracted sample is then added to the test device, which contains antibodies that specifically bind to SARS-CoV-2 antigens. These antibodies are typically immobilized on a test strip or membrane.
Detection: If SARS-CoV-2 antigens are present in the sample, they will bind to the antibodies on the test strip, forming an antigen-antibody complex. This complex then migrates along the test strip through capillary action.
Results Interpretation: The test strip contains a control line and a test line. The control line appears as a reference to confirm that the test is functioning correctly. If the test line, which contains specific antibodies for SARS-CoV-2 antigens, develops a visible line or color change, it indicates a positive result, indicating the presence of SARS-CoV-2 antigens in the sample. A lack of a test line indicates a negative result.



 Español
Español
 Français
Français
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 عربى
عربى