Jul 01,2022
Centrifuge tubes are widely used in various scientific and laboratory settings due to their importance and numerous benefits. Here are some key reasons why centrifuge tubes are important:
Sample Preparation: Centrifuge tubes play a crucial role in sample preparation for various laboratory procedures. They are used to collect, store, and centrifuge biological samples such as blood, urine, DNA, proteins, and cell cultures. The tubes are designed to withstand high-speed centrifugation, allowing for the separation of components based on their density or sedimentation properties.
Centrifugation: Centrifuge tubes are specifically designed to withstand the forces exerted during centrifugation. They are made from materials such as polypropylene, polycarbonate, or glass that can withstand high speeds and forces without deformation or breakage. This enables researchers to efficiently separate and isolate different components of a sample, such as cells, organelles, or supernatants, based on their sedimentation rates.
Sample Storage: Centrifuge tubes provide a secure and convenient method for sample storage. They are available in various sizes and volumes, allowing for the storage of different sample quantities. The tubes often come with airtight caps or seals to prevent contamination and maintain sample integrity during storage.
Chemical and Heat Resistance: Centrifuge tubes are designed to resist a wide range of chemical agents and temperatures. This makes them suitable for use in diverse laboratory applications, including biochemical assays, molecular biology, cell culture, and clinical diagnostics. The tubes can withstand exposure to solvents, acids, bases, and various reagents commonly used in laboratory experiments.
Versatility and Compatibility: Centrifuge tubes are compatible with a range of laboratory equipment, such as centrifuges, spectrophotometers, and liquid handling systems. Their standardized dimensions and compatibility with various accessories, such as adapters and racks, ensure seamless integration with different laboratory instruments and workflows.
Sample Tracking and Identification: Centrifuge tubes often feature labeling areas or caps with writable surfaces, allowing for easy sample identification and tracking. This is particularly important when handling multiple samples or conducting experiments that require precise documentation and traceability.
Safety and Contamination Prevention: Centrifuge tubes are designed to minimize the risk of sample contamination and ensure user safety. The tubes are often manufactured under stringent quality control measures to prevent leaks, breakage, or release of hazardous materials. Additionally, some centrifuge tubes may feature safety features such as leak-proof caps or biohazard symbols to promote safe handling and disposal.
Standardization and Reproducibility: The use of standardized centrifuge tubes promotes consistency and reproducibility in laboratory experiments. Researchers can rely on the consistent performance and specifications of centrifuge tubes, ensuring reliable results and comparisons across different studies or laboratories.
Overall, centrifuge tubes are essential tools in scientific research, clinical diagnostics, and various laboratory applications. Their importance lies in their ability to collect, store, and process samples efficiently while maintaining sample integrity, safety, and compatibility with laboratory equipment.Meanwhile,Centrifuge tubes are cylindrical containers designed to hold liquid samples during centrifugation. They typically have a tapered or conical shape with a closed bottom and an open top. Here is a breakdown of the structure of a centrifuge tube:
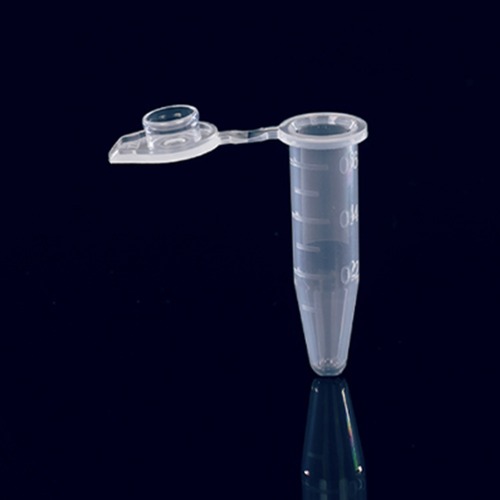
Body: The main body of the centrifuge tube is cylindrical in shape, with a tapering or conical design towards the bottom. The body is transparent or translucent, allowing users to observe the contents of the tube during centrifugation or other laboratory procedures.
Graduations: Many centrifuge tubes have graduated markings or volume indicators on the side of the tube. These graduations help in accurate measurement and dispensing of liquid samples. The graduations are usually marked in milliliters (mL) or other volume units.
Rim: The open top of the centrifuge tube has a rim or lip that provides stability and facilitates easy handling. The rim may have notches or grooves that allow for the attachment of caps or seals to secure the tube and prevent sample leakage or contamination.
Cap: Centrifuge tubes often come with removable caps or seals that fit tightly over the open end of the tube. The caps help maintain sample integrity by providing an airtight or leak-proof seal. Some caps may have additional features such as O-rings, pierceable membranes, or snap closures for easy access or sample manipulation.
Bottom: The bottom of the centrifuge tube is typically closed and rounded. It provides structural support to the tube and allows for stable placement in centrifuge rotors. The closed bottom prevents sample leakage and ensures proper sample separation during centrifugation.
Material: Centrifuge tubes are commonly made from materials such as polypropylene (PP), polycarbonate (PC), or glass. These materials are chosen for their transparency, chemical resistance, and ability to withstand high speeds and forces during centrifugation.
External Ribs: Some centrifuge tubes have external ribs or grooves along the body. These ribs enhance grip and provide better handling of the tube, especially when wearing gloves or working in wet conditions.
Labeling Area: Many centrifuge tubes have a designated area on the side or cap for labeling or marking purposes. This allows users to easily identify and track samples, record important information, or apply barcode labels for automated sample tracking systems.
The structure of centrifuge tubes may vary slightly depending on the manufacturer and specific design features. However, the general structure described above is common across most centrifuge tubes, ensuring their functionality and compatibility with centrifuge rotors and other laboratory equipment.



 Español
Español
 Français
Français
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 عربى
عربى