Jul 01,2022
PCR tubes, also known as PCR (polymerase chain reaction) test tubes or reaction tubes, are used in various laboratory applications, such as DNA amplification, gene cloning, and sequencing. The production steps for PCR tubes generally involve the following processes:
Material selection: The first step in the production of PCR tubes is the selection of the appropriate materials. PCR tubes are typically made of polypropylene (PP), which is a thermoplastic polymer that is resistant to chemicals and high temperatures.
Injection molding: The selected material is then molded into the shape of the PCR tube using an injection molding machine. The machine heats the plastic to a molten state and injects it into a mold, which is then cooled to form the desired shape.
Trimming and finishing: Once the PCR tubes are formed, they are trimmed and finished to remove any excess plastic and ensure that they meet the required specifications. This process may involve using cutting tools, grinders, or other finishing tools.
Sterilization: The PCR tubes are then sterilized to ensure that they are free from any contaminants that may affect the accuracy of the test results. Sterilization methods may include radiation, ethylene oxide gas, or autoclaving.
Packaging: Once the PCR tubes are sterilized, they are packaged in a sterile environment and sealed to prevent contamination. The tubes may be packaged in individual units, or in larger quantities, depending on the specific requirements of the application.
Overall, the production of PCR tubes involves several steps, including material selection, injection molding, trimming and finishing, sterilization, and packaging. Each step is critical to the production of high-quality PCR tubes that meet the specific requirements of the laboratory application.Meanwhile,PCR (polymerase chain reaction) tubes are small, cylindrical tubes used in molecular biology and genetics for a variety of applications, such as DNA amplification, gene cloning, and sequencing. PCR tubes can be classified based on various criteria, including:
Tube material: PCR tubes can be made of different materials, including polypropylene (PP), polycarbonate (PC), and other plastics. PP is the most commonly used material for PCR tubes due to its chemical resistance, low cost, and ability to withstand high temperatures.
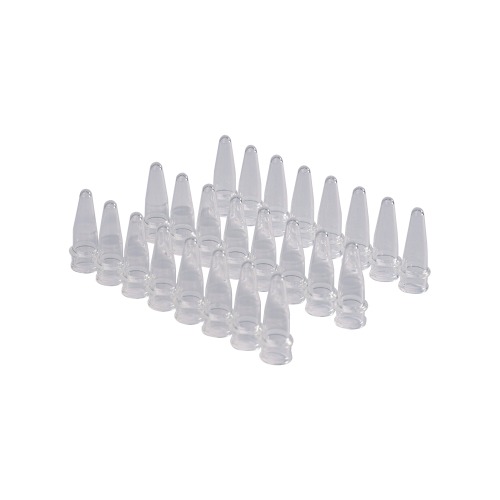
Tube format: PCR tubes are available in different formats, such as individual tubes, strips, or plates. Individual tubes are single tubes that can hold a specific volume of liquid, while strips are a row of connected tubes that can be separated as needed. PCR plates have multiple wells and are used for high-throughput applications.
Tube capacity: PCR tubes come in different capacities, ranging from 0.2 mL to 2 mL. The most common sizes are 0.2 mL and 0.5 mL.
Tube closure: PCR tubes can have different types of closures, including screw caps, snap caps, and flat caps. Screw caps provide a secure seal and can be used for long-term storage, while snap caps are easier to use but may not provide as tight of a seal.
Tube color: PCR tubes can be transparent or colored, with different colors used to indicate different samples or applications.
Overall, the classification of PCR tubes can be based on the tube material, format, capacity, closure, and color, among other criteria. The choice of PCR tube will depend on the specific application, the volume of the sample, and other factors such as compatibility with other laboratory equipment.




 Español
Español
 Français
Français
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 عربى
عربى