Jul 01,2022
Centrifuge tubes are commonly made from various materials, each offering different properties and benefits. The most common materials used for centrifuge tubes include:
Polypropylene (PP): Polypropylene is the most widely used material for centrifuge tubes. It is highly resistant to chemicals, making it suitable for a wide range of applications. PP centrifuge tubes are also autoclavable, which means they can be sterilized using high-temperature steam.
Polyethylene (PE): Polyethylene centrifuge tubes are another popular choice. They are more flexible than PP tubes and are often used for less aggressive centrifugation processes or for storage purposes.
Polycarbonate (PC): Polycarbonate centrifuge tubes are known for their excellent clarity, making them suitable for applications requiring visual observation of the contents. They are durable and can withstand high centrifugal forces.
Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET): PET centrifuge tubes are commonly used for low-speed centrifugation and are often disposable. They are not suitable for high-speed applications.
Glass: In some cases, glass centrifuge tubes are used for specialized applications requiring high chemical resistance or when centrifugation at high temperatures is necessary. However, glass tubes are more fragile than plastic alternatives and may not be suitable for all centrifugation processes.
Besides,Centrifuge tubes offer several advantages that make them indispensable tools in various scientific, medical, and research fields. Some of the key advantages of centrifuge tubes include:
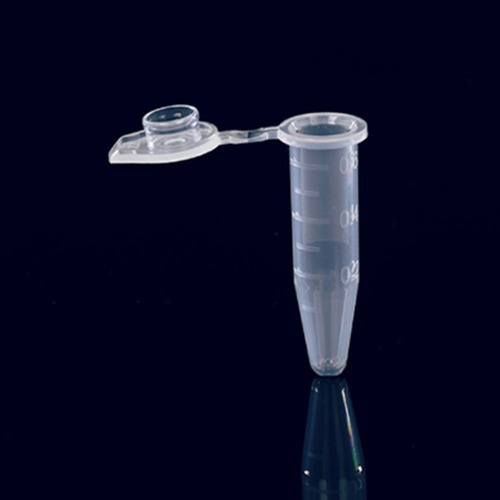
Sample Separation: Centrifuge tubes are designed to hold samples during centrifugation, a process that uses centrifugal force to separate components based on their density. This separation technique is crucial in various applications, including DNA extraction, cell isolation, and blood sample preparation.
Convenient Sample Storage: Centrifuge tubes come in various sizes, ranging from a few milliliters to several milliliters. They provide a secure and organized way to store samples, making them easy to handle and transport.
Wide Range of Materials: Centrifuge tubes are available in different materials, such as polypropylene, polyethylene, polycarbonate, and glass. This versatility allows users to select tubes suitable for their specific needs, considering factors like chemical compatibility, temperature resistance, and centrifugation speed requirements.
Autoclavability: Many centrifuge tubes, especially those made from polypropylene, can withstand autoclaving, which is a sterilization process using high-temperature steam. This allows for safe and efficient sample preparation, especially in microbiology and molecular biology laboratories.
Graduated Marks: Centrifuge tubes often have graduated marks on the side, allowing users to measure the volume of the sample accurately. This feature is particularly useful when precise volumes are required for experiments or assays.
Leak-Proof Sealing: Centrifuge tubes typically have secure sealing caps or closures, preventing sample leakage during centrifugation or storage. This ensures the integrity of the samples and prevents contamination between different samples.
Compatibility with Centrifuge Machines: Centrifuge tubes are designed to fit into various types of centrifuge machines, allowing for easy and standardized sample processing. They come in various tube shapes and sizes, including conical, round-bottom, and self-standing tubes, to suit different rotor types.
Versatile Applications: Centrifuge tubes find applications in a wide range of fields, including clinical diagnostics, research, biotechnology, pharmaceuticals, and environmental testing. They are essential tools in laboratories where sample preparation and analysis are routine tasks.
Cost-Effective: Centrifuge tubes are generally affordable and disposable, making them cost-effective for one-time use or for handling hazardous or infectious materials. For repeated use, reusable centrifuge tubes can be autoclaved and sterilized multiple times, extending their lifespan.



 Español
Español
 Français
Français
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 عربى
عربى