Jul 01,2022
The principle behind low-retention manual pipette tips is to reduce the adhesion or surface tension between the liquid sample and the inner surface of the pipette tip. This reduces the tendency of the sample to stick to the walls of the tip, minimizing liquid retention and ensuring accurate and precise sample delivery.
The low-retention effect is achieved through specific surface treatments or additives during the manufacturing process of the pipette tips. Here are some common methods used to achieve low retention in manual pipette tips:
1. Hydrophobic Surface Treatment: A hydrophobic surface treatment is applied to the inner surface of the pipette tip. This treatment creates a non-wetting surface, which repels the liquid sample and reduces adhesion. As a result, the liquid slides off the walls of the pipette tip more easily, leaving minimal residue.
2. Special Coatings: Some pipette tips are coated with special materials or polymers that have low surface tension. These coatings create a slippery surface that minimizes liquid adhesion and enhances sample release.
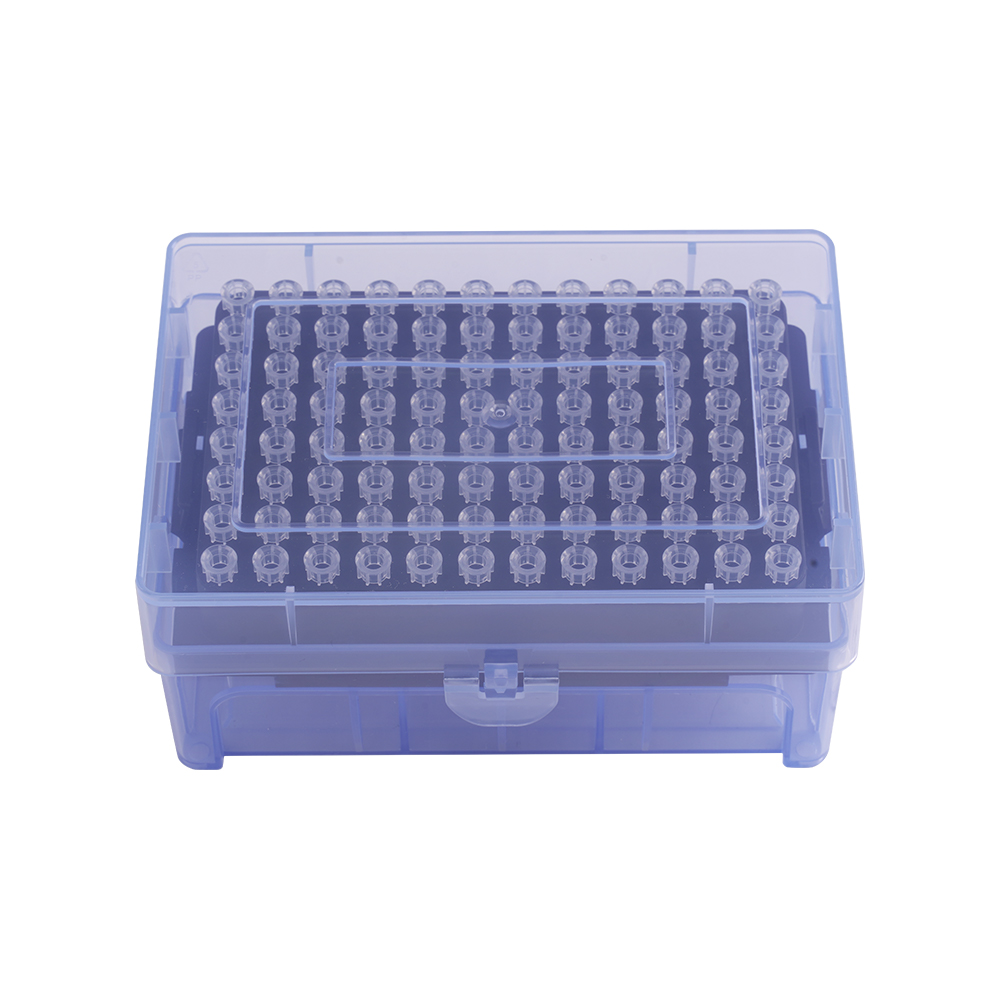

3. Additives in the Material:During the manufacturing process, low-retention additives or materials can be mixed into the plastic used to make the pipette tips. These additives alter the surface properties of the material, reducing its affinity for the liquid sample.
The benefits of low-retention pipette tips are significant, especially when handling small volumes or precious samples. By minimizing sample retention, these tips ensure accurate and precise liquid transfer, reducing the risk of sample loss and improving the reproducibility of experimental results.
Low-retention pipette tips are particularly useful in applications such as PCR, qPCR, DNA/RNA amplification, protein assays, and any assay involving small volumes and critical measurements. They are also valuable when working with viscous liquids, volatile solvents, or samples with surfactants that tend to stick to standard pipette tips.


 Español
Español
 Français
Français
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 عربى
عربى