Jul 01,2022
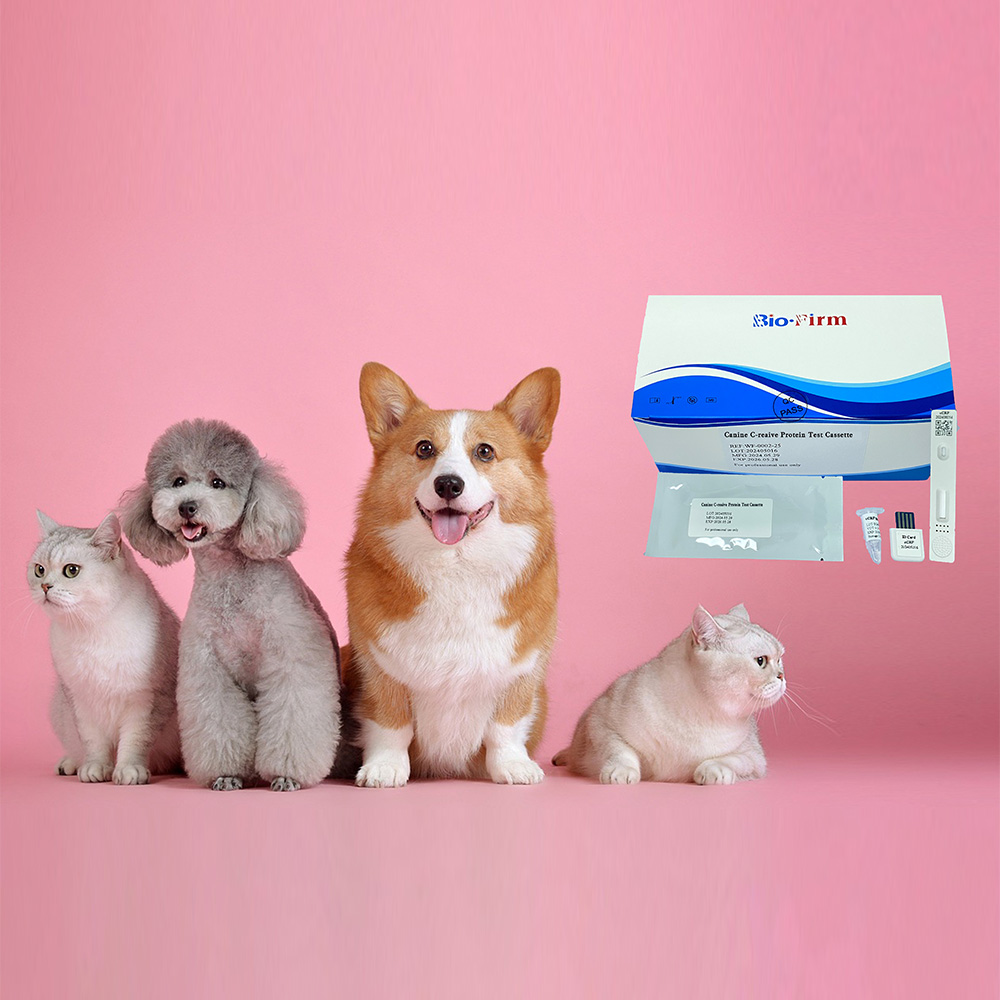
The key performance metrics for veterinary fluorescence immunoassays include several critical parameters that determine their accuracy, reliability, and overall effectiveness in diagnostic applications. Here are the primary metrics:
Key Performance Metrics
Limit of Detection (LOD):
Definition: The lowest concentration of an analyte that can be reliably detected but not necessarily quantified.
Importance: Determines the assay’s ability to detect low-abundance biomarkers or pathogens, which is crucial for early diagnosis and monitoring of diseases.
Limit of Quantification (LOQ):
Definition: The lowest concentration of an analyte that can be quantitatively measured with acceptable precision and accuracy.
Importance: Ensures that results at low concentrations are not only detectable but also reliably quantifiable.
Dynamic Range:
Definition: The range of analyte concentrations over which the assay provides accurate, linear, and reliable measurements.
Importance: Indicates the assay’s capability to measure both low and high concentrations of analytes without compromising accuracy, which is essential for detecting a wide range of conditions.
Precision:
Definition: The degree of repeatability or reproducibility of the assay results when the same sample is tested multiple times under the same conditions.
Metrics: Usually expressed as the coefficient of variation (CV) or standard deviation (SD).
Importance: High precision ensures consistent and reliable results, which is critical for monitoring disease progression and treatment response.
Accuracy:
Definition: The closeness of the assay results to the true value or standard reference.
Importance: High accuracy ensures that the assay provides true measurements of analyte concentrations, which is crucial for correct diagnosis and treatment decisions.
Sensitivity:
Definition: The ability of the assay to correctly identify the presence of an analyte (true positives).
Importance: High sensitivity reduces the likelihood of false negatives, ensuring that affected animals are correctly identified.
Specificity:
Definition: The ability of the assay to correctly identify the absence of an analyte (true negatives).
Importance: High specificity reduces the likelihood of false positives, ensuring that healthy animals are not misdiagnosed.
Robustness:
Definition: The ability of the assay to remain unaffected by small, deliberate variations in method parameters.
Importance: Indicates the assay’s reliability under different conditions, such as variations in sample type, operator handling, or environmental factors.
Throughput:
Definition: The number of samples that can be processed in a given period.
Importance: High throughput is important for veterinary clinics and laboratories that need to process large volumes of samples efficiently.

Time to Result:
Definition: The time required to obtain a result from sample preparation to final readout.
Importance: Rapid results are crucial for timely decision-making in clinical settings.
Stability:
Definition: The duration for which the assay components and reagents remain stable and effective under specified storage conditions.
Importance: Ensures the reliability and consistency of the assay over time, reducing the need for frequent re-validation.
Practical Considerations
Interference and Cross-reactivity:
Definition: The effect of other substances in the sample that may affect the assay’s performance.
Importance: Low interference and cross-reactivity are essential for ensuring that the assay specifically measures the target analyte without interference from other sample components.
Ease of Use:
Definition: The simplicity and user-friendliness of the assay protocol.
Importance: Assays that are easy to use reduce the likelihood of user error and improve consistency in results.
Cost-effectiveness:
Definition: The overall cost of running the assay, including reagents, equipment, and labor.
Importance: Cost-effective assays make advanced diagnostics more accessible to veterinary practices.
By optimizing these performance metrics, veterinary fluorescence immunoassays can provide accurate, reliable, and timely diagnostic information, supporting better clinical decision-making and improving animal health outcomes.


 Español
Español
 Français
Français
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 عربى
عربى